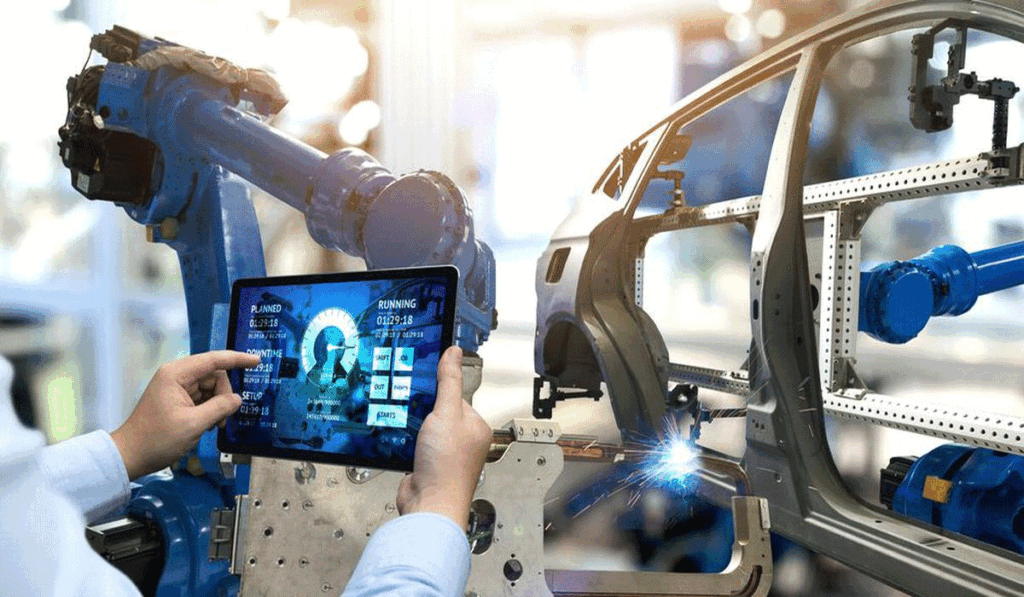
Traditional factories that once relied heavily on manual labor and conventional machinery are now embracing digital technologies.

These advancements are helping companies produce faster, smarter, and more efficiently while keeping up with an increasingly competitive global market. The digital transformation of manufacturing is no longer optional it’s essential for staying relevant in the era of Industry 4.0.
In this “Simplifying Transformation Streamlining Business Projects” guide, we’ll cover industry insights, production digitization strategies, factory workflow optimization, automation and IoT techniques, and long-term growth plans for smart manufacturing.
The Era of Traditional Manufacturing
Traditional manufacturing relies on human labor and conventional machines. Every step, from raw material processing to assembly, is often done separately, with limited coordination. This approach can be slow and prone to errors, leading to wasted materials, extra costs, and defective products.
Data management is also a challenge. Many factories still track production manually, making it difficult for managers to monitor efficiency or quality in real-time. Decision-making often becomes slower due to the lack of integrated information across departments.
Despite its limitations, traditional manufacturing has historical value. Skilled labor adds craftsmanship and quality to specialized or high-value products, where human touch is crucial. Some factories maintain these methods for products where uniqueness matters more than speed.
Automation and Digitalization
Digitalization has revolutionized manufacturing processes. Smart computers and sensors now allow real-time monitoring of every production stage. Robotics can handle repetitive tasks, reducing human error and speeding up production. Efficiency has increased dramatically because of these innovations.
Modern production software integrates data across all operations. Managers can track raw materials, machine usage, and production schedules in one system. This makes it easier to respond to changing customer demands and make faster, smarter decisions.
The Internet of Things (IoT) and predictive sensors also prevent machine breakdowns before they happen. Predictive maintenance reduces downtime and repair costs, proving that digitalization enhances efficiency while lowering risks.
Read Also: Business Strategy for Competitive Advantage in the Global Era
Benefits of Going Digital

One of the biggest benefits of digital manufacturing is better product quality. Automated monitoring and sensor-based inspections reduce defective products and ensure consistent standards that meet modern consumer expectations.
Digitalization also provides production flexibility. Smart factories can adapt their production lines to meet changing demands, even for custom orders. This allows companies to offer personalized products without losing efficiency.
Sustainability is another advantage. Real-time monitoring of energy and materials reduces waste, saving money and supporting environmental responsibility. Digital factories are not just faster they’re greener too.
Challenges of Digital Transformation
Digital transformation comes with challenges. Initial investments in hardware, software, and employee training can be significant. Small and medium-sized enterprises may struggle to keep up with fast technological changes.
Cultural change within organizations is equally important. Employees need training and support to operate new systems effectively. Without human engagement, even the most advanced technology cannot reach its full potential.
A gradual implementation strategy works best. Companies can start by digitizing critical processes first, while building internal capabilities and strengthening IT infrastructure. This approach reduces risks and ensures the benefits of new technology are fully realized.
The Future of Manufacturing
The future of manufacturing is intelligent, fast, and sustainable. Companies that combine technology, skilled workers, and data-driven processes can improve efficiency, quality, and flexibility simultaneously.
Challenges such as cost and employee adaptation are real, but the long-term advantages outweigh the risks. Businesses that embrace digital transformation early will have a competitive edge in the global market.
Ultimately, manufacturing is moving from traditional factories to smart plants. Those who innovate and adopt digital solutions will lead the industry, shaping a smarter, more efficient, and sustainable future for production worldwide.